Overview
The Command Line Ingest feature allows you to run many of Autopsy's functions from the command line. You can add data sources to cases, choose which ingest modules to run, and automatically generate a report. When complete, these cases can be opened as normal or you can simply use the reports and other output without opening Autopsy.
Configuration
Go to Tools->Options and then select the "Command Line Ingest" tab.
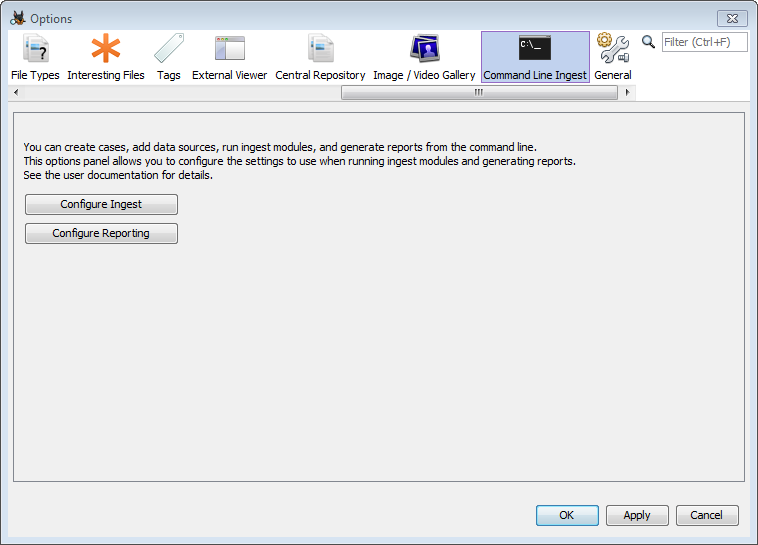
Use the ingest module settings to configure how you want to run ingest. This is the same as normal ingest module configuration - choose a file filter then enable or disable the individual ingest modules, changing their settings if desired. Press "OK" to save your settings.
Use the report module settings to choose and configure a report type. Only the selected report type will be generated. Configuration is generally the same as normal report generation with some slight differences. This is mainly seen in places where your options are dependent on the open case, such as choosing tags to report on or interesting file set names to include. For example, the HTML report normally allows you to choose specific tags to include but for command line ingest it will only have the option to include all tags.
If you would like to create or open multi-user cases, you'll need to configure the multi-user settings.
Command Options
In a command prompt, navigate to the Autopsy bin folder. This is normally located at "C:\Program Files\Autopsy-version\bin".
The table below shows a summary of the command line operations. You can run one or more at a time, though you must always either create a case or open an existing case.
| Operation | Command(s) | Parameter(s) | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create New Case | --createCase | --caseName --caseBaseDir --caseType (optional) | --createCase --caseName="test5" --caseBaseDir="C:\work\cases" --createCase --caseName="test_multi" --caseBaseDir="\\WIN-2913\work\cases" --caseType="multi" |
| Open Existing Case | --caseDir | --caseDir="C:\work\Cases\test5_2019_09_20_11_01_29" | |
| Add a Data Source | --addDataSource --runIngest (optional) | --dataSourcePath | --addDataSource --dataSourcePath="R:\work\images\small2.img" --runIngest |
| Run Ingest on Existing Data Source | --runIngest | --dataSourceObjectId | --runIngest --dataSourceObjectId=1 |
| Generate Reports | --generateReports | --generateReports | |
| Create List of Data Sources | --listAllDataSources | --listAllDataSources |
More details on each operation along with additional examples are given below.
Creating and Opening Cases
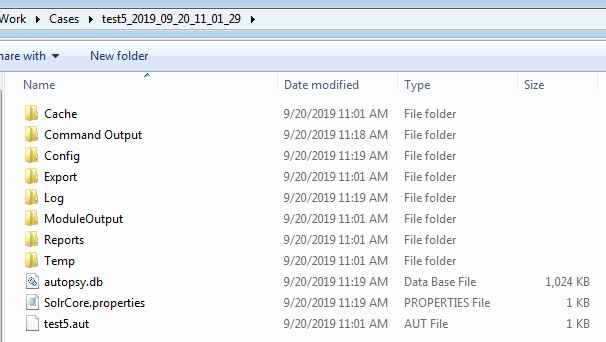
You will always need to either create a case or give the path to an existing case. When creating a case, the current timestamp will be added to the case name. For example, running this command:
autopsy64.exe --createCase --caseName="test5" --caseBaseDir="C:\work\cases"
could create a case folder "test5_2019_09_20_11_01_29". Note that even though a timestamp is added to the name, the –caseName field must be unique for each run.
By default all cases will be single user. If you would like to create a multi-user case you'll need the -caseType field. You should also use the network path to your case folder so the services can access it:
autopsy64.exe --createCase --caseName="test_multi" --caseBaseDir="\\WIN-2913\work\cases" --caseType="multi"
Once a case is created you will need to use the full path to the case instead of the case name and base folder. For example, if we created the empty case "test5" as above, we could use the following command to add a data source to it:
autopsy64.exe --caseDir="C:\work\Cases\test5_2019_09_20_11_01_29" --addDataSource --dataSourcePath="R:\work\images\small2.img"
The case type (single or multi-user) does not have to be specified when opening a case.
Adding a New Data Source and Running Ingest
You can add a data source to a new case or an existing case using the –addDataSource option and then giving the path to the data source. If you use the –runIngest option, the ingest modules you selected in the configuration step will be run on the data source. Both disk images and logical files are supported. You can only add one data source at a time.
In this example, we'll create a new case named "test6" and add the data source "blue_images.img".
autopsy64.exe --createCase --caseName="test6" --caseBaseDir="C:\work\cases" --addDataSource --dataSourcePath="R:\work\images\blue_images.img"
And here we'll add another data source ("green_images.img") to the case we just made and run ingest on it. Note that ingest will only run on the new data source ("green_images.img"), not the one already in the case ("blue_images.img").
autopsy64.exe --caseDir="C:\work\cases\test6_2019_09_20_13_00_51" --addDataSource --runIngest --dataSourcePath="R:\work\images\green_images.img"
Finally we'll add a folder ("Test files") as a logical file set to a new case ("test9").
autopsy64.exe --createCase --caseName="test9" --caseBaseDir="C:\work\Cases" --addDataSource --dataSourcePath="R:\work\images\Test files" --runIngest
Running Ingest on an Existing Data Source
You can run ingest on a data source already in the case if you know its object ID. To find this, go to the case folder and open the "Command Output" folder.
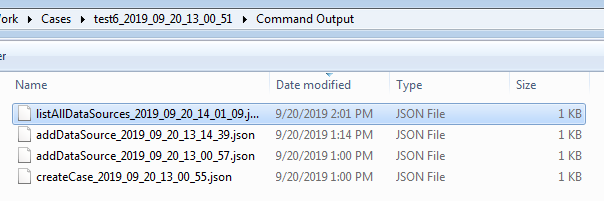
If you've run with the –listAllDataSources option, there will be at least one file starting "listAllDataSources". Open the most recent one - the format will be similar to this:
{
"@dataSourceName" : "blue_images.img",
"@dataSourceObjectId" : "1"
} {
"@dataSourceName" : "green_images.img",
"@dataSourceObjectId" : "84"
}
You can also look through the addDataSource files to find the one corresponding to the file you want to ingest. The format will be the same. Once you know the data source object ID, you can use the –dataSourceObjectId option to specify it. For example, this will run ingest on "blue_images.img":
autopsy64.exe --caseDir="C:\work\cases\test6_2019_09_20_13_00_51" --runIngest --dataSourceObjectId=1
Generating Reports
You can generate a report on the case using the –generateReports option. You can select which report type to export through the Autopsy options panel (see the configuration section). This option can be run alone or at the same time as you're processing a data source. In this example we're adding a new data source ("small2.img") and generating a report.
autopsy64.exe --caseDir="C:\work\cases\test6_2019_09_20_13_00_51" --addDataSource --dataSourcePath="R:\work\images\small2.img" --runIngest --generateReports
Listing All Data Sources
You can add the –listAllDataSources at any time to output a list of all data sources currently in the case along with their object IDs, to be used when running on an existing data source. This command can even be run alone with just the path to the case.
autopsy64.exe --caseDir="C:\work\cases\test6_2019_09_20_13_00_51" --listAllDataSources
Running Autopsy
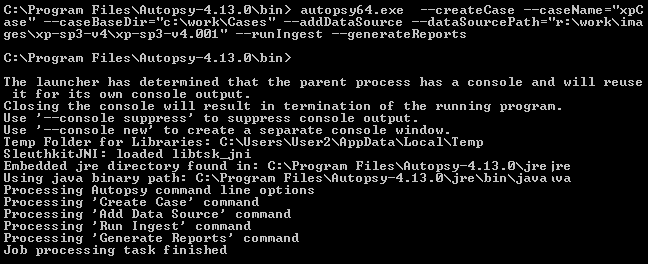
Once you determine which parameters you need, it's time to run Autopsy. In the example below we're creating a new case ("xpCase"), adding a data source to it ("xp-sp3-v4.001"), running ingest and generating a report. The report type was configured earlier to be an HTML report.

If you've entered everything correctly, Autopsy will load and you'll see this dialog in the middle of the screen:
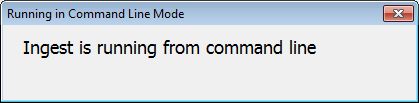
If you instead see the normal case open dialog, it most likely means that your command line is malformed. Verify that there are no typos and that you have the appropriate parameters for the operation(s) you're attempting.
If everything works correctly, you'll see a log of the processing being done and Autopsy will close when finished.
Viewing Results
You can open the case created on the command line like any other Autopsy case. Simply go to "Open Case" and then browse to the output folder you set up in the Configuration section and look for the folder starting with your case name. It will have a timestamp appended to the name you specified.
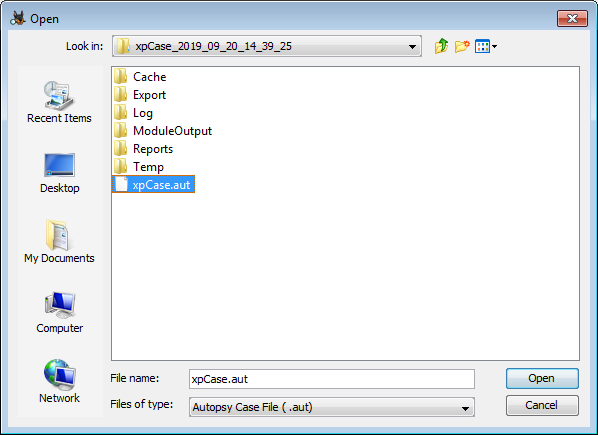
If you are only interested in the reports then you don't need to open Autopsy. You can just browse to the "Reports" folder in the case and access the reports directly.
